QuickTime
Apple’s QuickTime software is widely used for handling movies and other kinds of data on both Mac OS and Windows-based computers. With QuickTime, even a relatively slow computer can handle video or sound material that changes rapidly in real time. And on the Mac OS, you can play movies and perform other QuickTime operations in applications that weren’t designed for such purposes.
- To enable QuickTime in the Classic Mac OS you must install the QuickTime™ file and related files in your Extensions folder, inside the System Folder, and then restart the computer.
Alternatives to QuickTime
RealPlayer (RealNetworks), accommodates various files, as well as real-time streaming of sound and video via proprietary formats such as RealAudio, RealVideo, RealPix and RealText. The later RealOne Player for Mac OS X works with AIFF, AU, AVI, MP2, MP3, SMIL, SWF and WAV files, although these are also accommodated by modern versions of QuickTime.
- QuickTime is available for Windows but doesn’t fully support some PC file formats, requiring you to use alternative software, such as Video for Windows (VfW) or ActiveMovie.
 What QuickTime Provides
What QuickTime Provides
With QuickTime installed you can view or listen to various files containing images, movies, sounds and music. In the Mac OS you can use any QuickTime-aware application, such as PictureViewer or QuickTime Player, to look at these files, as well as:-
In a QuickTime-aware Application you can:-
- View QuickTime movies, complete with any available sound track
- Listen to a MIDI music sequence, which can form part of a movie. This can be played on the computer itself via Roland’s General MIDI (GM) sounds, as supplied, or you can use other protocols and an external synthesiser connected via a MIDI interface adaptor. Suitable protocols include the Core MIDI element of Mac OS X, as well as FreeMIDI (Mark of the Unicorn), MIDI Manager (Apple) or Open Midi System (Opcode) in Mac OS 9.x.
- Open or import all the file formats that are acceptable to QuickTime, as well as the sound tracks stored on an audio CD or the musical sequence in a MIDI file or Karaoke file.
- Export files in all formats supported by QuickTime, with the option of using one of many compression codecs that reduce the size of a file while retaining acceptable quality.
- Create or edit sound samples in a sound application and adjust the overall volume or balance. Sampling can use 8 or 16 bits, be at any sample rate and be in mono or stereo.
- Modify imported movies by adjusting the hue, saturation, brightness, sharpness, black level or white level content. The result can be saved in a new document.
- The Roland GM sounds for Mac OS 9.x are in the QuickTime™ Musical Instruments file.
- QuickTime version 6.5.1 or higher includes the full GM sound set.
In All Applications you can:-
- Add a preview image to a document from within an application’s Open dialogue.
- Automatically employ QuickTime compression for handling PICT files.
- QuickTime in the Classic Mac OS also ensures that the correct icon, type code and creator code is provided for any foreign file that has a recognised filename extension.
- You can view QuickTime content in your Web browser by installing the the QuickTime Plugin file. In the Mac OS 9.x this must be located in your Internet Plug-ins folder.
QuickTime Pro
Unfortunately, the free version of QuickTime supplied with the Mac OS doesn’t have all of the features described above. Most significantly, it lacks the ability to export files in different formats from a QuickTime-aware application. However, you can upgrade your existing version of QuickTime to the full product, known as QuickTime Pro, by simply purchasing a key code from Apple.
- QuickTime 2.5 and MoviePlayer 2.5 on the Classic Mac OS incorporate some of the features found in QuickTime Pro, unlike later non-activated versions of QuickTime. In addition, MoviePlayer 2.5 keeps these abilities when used with newer versions of QuickTime. If you want to keep your original MoviePlayer 2.5 you should copy it onto a backup disk before installing a newer version of QuickTime. If you don’t, the Mac OS Installer will delete it!
Supported Formats
Version 5 of QuickTime plays over 200 different types of media files and data. It supports a huge range of file formats, some of which are used with real-time streaming on the Internet. For this reason, QuickTime also accommodates both Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) and Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP), both of which are required for such streaming.
The most significant file formats are listed in the tables shown below. In most instances, the filename extensions shown are the common three-character variety, although alternatives are used.
 Graphics
Graphics
| Description | Ext | Notes |
|---|
| 3DMF | .3df | QuickDraw 3D image |
| BMP * | .bmp | Windows bitmap |
| Cubic QT VR Panorama | - | Virtual Reality (VR) with movement in all directions |
| FlashPix | .fpx | Open standard for fast digital images |
| GIF | .gif | Traditional Web bitmap |
| JPEG * | .jpg | Photographic bitmap with lossy compression |
| MacPaint * | .mac | Mac OS bitmap format (outdated) |
| Photoshop * | .psd | Photoshop document (bitmap) |
| PICT * | .pct | Classic Mac OS bitmap or vector image |
| PNG * | .png | Modern Web bitmap |
| QuickTime Image * | .qif | Native QuickTime format (QTIF) |
| SGI Image * | .sgi | Silicon Graphics bitmap |
| Shockwave Flash 4 | .swf | Web vector format, also used for animations |
| TGA * | .tga | Targa bitmap |
| TIFF * | .tif | Standard DTP bitmap |
* Also available for file export
- QuickTime version 6 or higher also supports JPEG 2000 compression, providing higher quality images in smaller files than the standard JPEG format.
 Movies
Movies
| Description | Ext | Notes |
|---|
| AVI * | .avi | Windows format |
| DV Stream * | .dv | Digital Video (DV), used with VCRs |
| FLC * | .flc | FLC and FLI formats |
| Image Sequence * | - | Sequence of graphics files (export only) |
| Shockwave Flash 4 | .swf | Vector animation for Web |
| MPEG-1 • | .mpg | Quarter-size image, high-quality sound (Mac support only) |
| MPEG-2 • | .mpg | Full-size image, high-quality sound as used on DVDs |
| MPEG-4 | .mp4 | Advanced multimedia format |
| OMF | - | Open Media Framework version of AVI |
| OpenDML | - | High-quality standard from Avid |
| PICS | .pcs | Sequence of Classic Mac OS PICT images |
| QuickTime Movie * | .mov | Native QuickTime format |
* Also available for file export
• Requires QuickTime™ MPEG Extension file in the Classic Mac OS
- QuickTime accepts signals conforming to the American NTSC, European PAL and French SECAM television standards at frame rates of 8, 10, 12, 15, 24, 25 and 30 frames per second (frm/s). It also incorporates filtering that accommodates material originating from a television (TV) receiver, video disk or video cassette recorder (VCR).
- Version 6 of QuickTime meets the Internet Streaming Media Alliance 1.0 standard for playing MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, Flash 5 and DVCPRO (PAL) movies. MPEG-4 provides sound and picture quality close to that of Digital Video (DV) and is designed to replace proprietary streaming systems, including QuickTime and RealNetworks formats.
- Some QuickTime movie files only contain sound or musical data.
 Sound
Sound
| Description | Ext | Notes |
|---|
| AIFF * | .aif | Audio Interchange File Format, standard Apple format |
| Audio CD data | - | Sound track from CD (Mac support only) |
| MPEG Layer 2 | .mp2 | Used for MPEG-1 or MPEG-2 movies |
| MPEG Layer 3 | .mp3 | MP3 format used on Web |
| MPEG-4 | .m4a | MP4 file using Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) |
| ShoutCast MP3 | .mp3 | Sound streaming for the Internet |
| System 7 Sound * | .sfil | Standard Classic Mac OS sound |
| Sound Designer II | .sd2 | Used by application of same name |
| Wave * | .wav | Windows format |
| µLaw * | .au | Sun Audio format |
* Also available for file export
- Version 6 of QuickTime also supports Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) compression, forming part of the MPEG-4 standard and providing better quality than the MP3 format.
- QuickTime version 6.5.1 or higher provides an enhanced quality of encoding for AAC.
 Music and Others
Music and Others
| Description | Ext | Notes |
|---|
| Karaoke | .kar | MIDI musical sequence |
| MIDI * | .mid | MIDI musical sequence |
| Text | .txt | Plain text |
| Timecode | - | Duration of recording in hours, minutes, seconds and frames |
* Also available for file export
 QuickTime Codecs
QuickTime Codecs
The content of a document is often compressed to save space. Unfortunately, there are numerous different compression systems available, even within a single file format. So your applications must also be able to understand the compression system used in each document as well as the file format.
Codec and Filter Files
The software used to compress or decompress a file is known as a coder-decoder or codec. Many of these codecs are built into QuickTime itself, while others can be provided as separate files.
- Whenever you select Export in a QuickTime-aware application you’ll see a list of the available codecs in the Settings pop-up menu.
- Extra codecs for the Classic Mac OS must be placed in the QuickTime Extensions folder, within the Extensions folder, or (if you insist) inside the Extensions folder itself. These codec files, known as component extensions and identified by a type code of
thng, don’t modify the operating system, although they must be present at startup to be effective. - The codecs supplied with NetShow (Microsoft) and other applications can also be used with QuickTime, although some older varieties of codec may be ignored. You can try the following:- Indeo Video, Indeo Video 4, Intel Raw Video, MPEG Layer-3 Audio, MPG4, TR20d, VDOwave MS Video Decoder, VDOwave Video Decoder, VivoActive G723 Decoder, VivoActive Siren Decoder, VivoActive Video Decoder, Voxware MetaSound (PPC), Voxware MetaVoice (PPC), Voxware VDK v1.1.6 (PPC) (library file), Voxware VDK v1.1.w (PPC) (library file) and Windows Compressors.
- Not all codecs are suitable for creating files for use on a PC, even one that’s equipped with QuickTime. This is because all codecs used on a PC must be compatible with the Media Control Interface used in Windows. Fortunately, many codecs are suitable, including Apple BMP and Cinepak, as well as more modern offerings.
- Extra filter files can also be placed in QuickTime Extensions. Whenever you select Export in a QuickTime-aware application you’ll see these extra filters in the Filter section.
Determining an Unknown Codec
Sometimes, when opening an odd file format, QuickTime Player shows a white movie window and a dialogue saying something like Required compressor can’t be found. If this happens, leave the window open and select Get Info from under the Movie menu. Then set the pop-up menus as shown below. Hopefully, the Data Format information will help you obtain a suitable codec for your file.
Standard Codecs
QuickTime accepts files created using the following codecs:-
Graphics and Movies
| Codec | Notes |
|---|
| Animation * | Run length encoding (RLE) |
| Apple BMP * | Bitmap image, compatible with Classic Mac OS |
| Cinepak * | For high frame rates, may require powerful computer |
| Component Video * | High-quality YUV format |
| DV-NTSC * | Digital Video (American NTSC standard) |
| DV-PAL * | Digital Video (European PAL standard) |
| DVCPRO-PAL * | Professional Digital Video (European PAL standard) |
| Graphics * | Simple 8-bit images |
| H.261 * | High-quality video, fast decoding |
| H.263 * | Improved version of H.261, slower decoding |
| H.264/AVC * † | Advanced Video Coding (AVC) |
| Intel Indeo Video 3.2 | Older video compression system |
| Intel Indeo Video 4.4 | Older video compression system |
| Intel Raw | Older video system |
| Microsoft RLE | Run length encoding (RLE), as used in Windows |
| Microsoft Video 1 | Used in Windows computers |
| Motion JPEG A * | Broadcast-quality video |
| Motion JPEG B * | Variation of Motion JPEG A |
| None * | Large file size but highly compatible |
| Photo-JPEG * | Photographic images |
| Planar RGB * | Simple images |
| PNG * | General purpose, as used in PNG graphics files |
| Sorenson Video * | Powerful compression for Internet |
| Sorenson Video 3 * • | Development of above Sorenson Video 2 standard |
| TGA * | Used in TGA graphics files |
| TIFF * | Used in TIFF graphics files |
| Video | Optimised for real video images |
* Also available for file export
• Real-time coding not supported in QuickTime 5
† Mac OS X 10.4 or higher only
- Most of the these codecs aren’t used for graphics files, which have their own compression systems. However, any codec can be used in a QuickTime Image File (QTIF).
- The DivX codec, a variation of MPEG-4 technology devised by DivXNetworks that’s used in recent AVI files, isn’t currently supported by the Mac OS.
Sound
| Format | Notes |
|---|
| 24-bit Integer * | Linear coding, no compression |
| 32-bit Integer * | Linear coding, no compression |
| 32-bit Floating Point * | Linear coding, no compression |
| 64-bit Floating Point * | Linear coding, no compression |
| Adaptive Multi-Rate (AMR) * | ACELP-based predictive speech coding for GSM/G3PP phones |
| Advanced Audio Coding (AAC) * | Physcoacoustic music coding, MP4 standard |
| ALaw 2:1 * | 2:1 lossy compression |
| Apple Lossless *† | Lossless, CD quality using 60-70% of the data |
| Code Excited Linear Predictive (CELP) * | Predictive speech coding, MP4 standard |
| IMA 4:1 * | 4:1 lossy compression, audible effects |
| MACE 3:1 * | 3:1 lossy compression, audible effects |
| MACE 6:1 * | 6:1 lossy compression, highly audible effects |
| MP3 * | Physcoacoustic music coding |
| MS ADPCM | Microsoft, used on Windows computers |
| QDesign Music 2 * | Real-time music coding |
| Qualcomm Code Excited Linear (QCEL) * | Predictive speech coding |
| Qualcomm PureVoice * | 9:1 or 19:1 real-time speech coding |
| µLaw 2:1 * | 2:1 lossy compression |
* Also available for file export
† Similar to the Free Lossless Audio Codec (FLAC)
- Not all files support every codec. For example, an AVI file only accommodates ALaw or µLaw coding, a System 7 Sound file only uses ALaw, IMA, MACE or µLaw, a Wave file doesn’t need any compression and a µLaw file only accommodates Floating Point, ALaw or µLaw coding. However, any type of codec can be used in a movie file or AIFF.
 QuickTime and the Internet
QuickTime and the Internet
QuickTime lets you experience multimedia files received over the Internet, including real-time radio and television broadcasts sent using Real-Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP). To see such material in your Web browser you must install the QuickTime Plugin file. In the Classic Mac OS this file should be placed in the Internet Plug-Ins folder, inside the System Folder.
At the time of writing, the QuickTime plug-in supports the following files:-
| Graphic File | Ext | Mime Type |
|---|
| BMP image | .bmp | image/x-bmp |
| MacPaint image | .pntg, .pnt, .mac | image/x-macpaint |
| PICT image | .pict, .pic, .pct | image/pict |
| PICT image | .pict, .pic, .pct | image/x-pict |
| PNG image | .png | image/png |
| PNG image | .png | image/x-png |
| QuickTime image | .qtif, .qti | image/x-quicktime |
| SGI image | .sgi, .rgb | image/x-sgi |
| TGA image | .targa, .tga | image/x-targa |
| TIFF image | .tif, .tiff | image/tiff |
| TIFF image | .tif, .tiff | image/x-tiff |
| Movie File | Ext | Mime Type |
|---|
| AutoDesk Animator (FLC) | .flc, .fli | video/flc |
| MPEG media | .mpeg, .mpg * | video/x-mpeg |
| MPEG media | .mpeg, .mpg * | video/mpeg |
| QuickTime Movie | .mov, .qt | video/quicktime |
| Video For Windows (AVI) | .avi, .vfw | video/x-msvideo |
| Video For Windows (AVI) | .avi, .vfw | video/msvideo |
| Video For Windows (AVI) | .avi, .vfw | video/avi |
| Sound File | Ext | Mime Type |
|---|
| AIFF audio | .aiff, .aif, .aifc | audio/aiff |
| AIFF audio | .aiff, .aif, .aifc | audio/x-aiff |
| GSM audio | .gsm | audio/x-gsm |
| MP3 audio | .mp3 | audio/mpeg |
| MP3 audio | .mp3 | audio/x-mpeg |
| MP3 audio | .mp3 | audio/mp3 |
| MP3 audio | .mp3 | audio/x-mp3 |
| MP3 audio | .mp3 | audio/mpeg3 |
| MP3 audio | .mp3 | audio/x-mpeg3 |
| MPEG audio | .mpeg, .mpg • | audio/mpeg |
| MPEG audio | .mpeg, .mpg • | audio/x-mpeg |
| QUALCOMM PureVoice | .qcp | audio/vnd.qcelp |
| WAVE audio | .wav | audio/x-wav |
| WAVE audio | .wav | audio/wav |
| uLaw/AU audio | .au, .snd, .ulw | audio/basic |
| Music File | Ext | Mime Type |
|---|
| MIDI | .mid, .midi, .smf, .kar | audio/mid |
| MIDI | .mid, .midi, .smf, .kar | audio/x-midi |
| MIDI | .mid, .midi, .smf, .kar | audio/midi |
| Other File | Ext | Mime Type |
|---|
| RTSP stream descriptor | .rtsp, .rts | application/x-rtsp |
| SDP stream descriptor | .sdp | application/sdp |
| SDP stream descriptor | .sdp | application/x-sdp |
* Also .m15, .m1a, .m1s, .m1v, .m2v, .m75, .mp2, .mpa, .mpm, .mpv and others
• Also .m1a, .m1s, .mp2, .mpa, .mpm and others
©Ray White 2004.

 What QuickTime Provides
What QuickTime Provides What QuickTime Provides
What QuickTime Provides Graphics
Graphics Movies
Movies Sound
Sound Music and Others
Music and Others QuickTime Codecs
QuickTime Codecs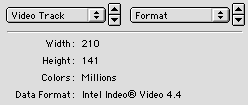
 QuickTime and the Internet
QuickTime and the Internet